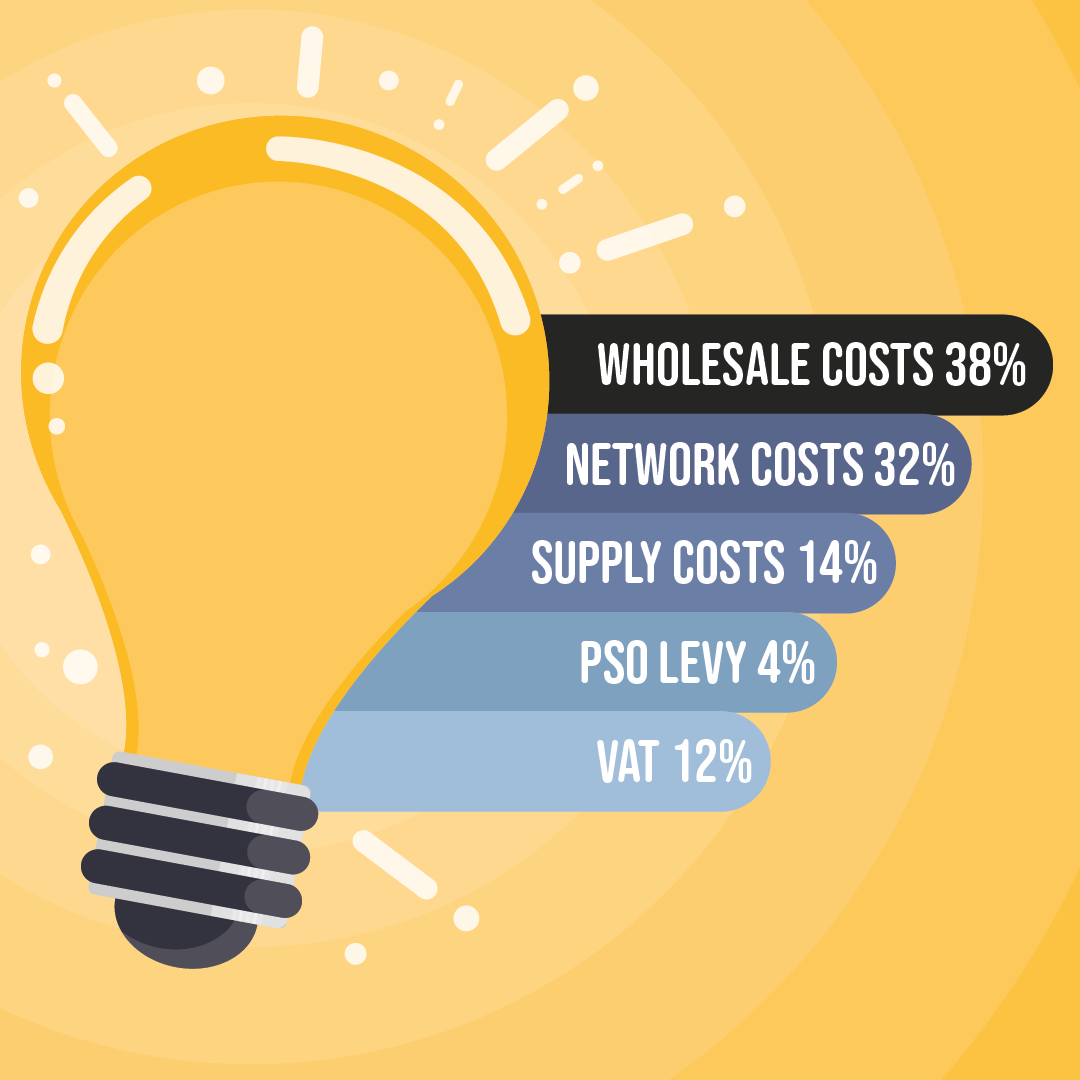
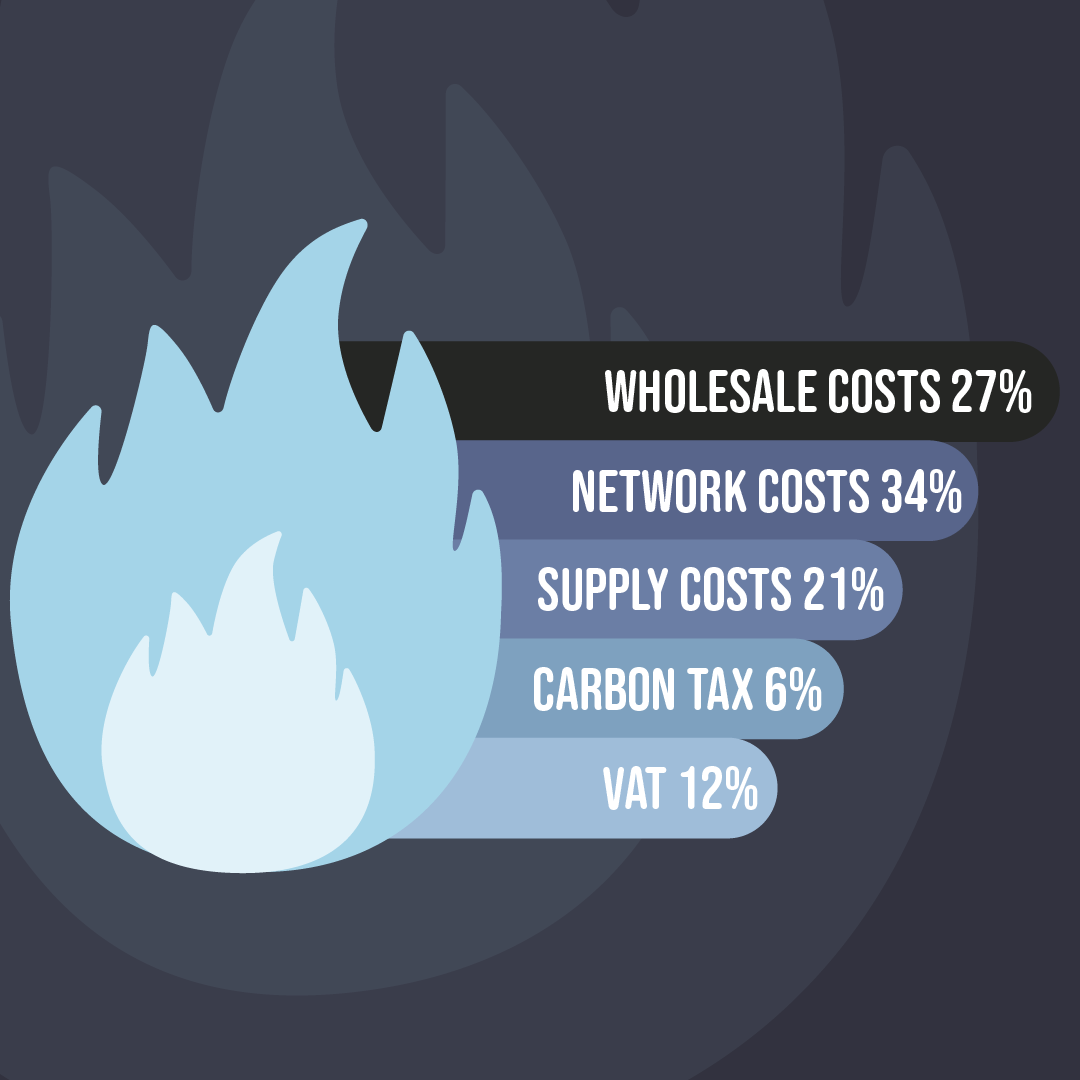
There are a range of costs and charges that go together to determine how much you end up paying for your home electricity and gas.
When prices change, we often hear these are driven by global uncertainty, wholesale costs or even the weather. But amidst these global issues it can be hard to appreciate the actual costs that go together to make up the price you are asked to pay.
So, in this guide we breakdown the main costs that make up an electricity and gas bill. And although the final price you pay will vary across suppliers (which is why it is good to switch) all supplier bills will be made up of the same types of costs.
In summary electricity and gas bills are made up of the main costs, as detailed below:
Wholesale costs
The biggest element of electricity and gas bills is the cost of purchasing wholesale energy by your supplier. For electricity the wholesale price accounts for nearly 40% of the average electricity bill whilst the wholesale gas price accounts for nearly 30% of the average gas bill in Ireland.
Network costs
Suppliers need to get the energy to your home through the gas and electricity distribution network and the cost of doing this are covered by Network Costs.
For electricity and gas there is a complex transmission and distribution network which moves energy around and ultimately to your home. These include the wires, pylons, pipework and the cost to safely manage the transmission and distribution network.
Energy network costs are the second largest component of your energy bill. The costs, charges and revenues that can be applied by network operators are set by the regulator (CRU.ie) in order to ensure security of supply, value for money and protect consumers.
Supply costs
Supply costs relate to the costs your supplier incurs to operate their business and manage the service that they provide to you the customer. This will include, for example, the costs of billing, meter reading, customer service, offices, salaries and IT systems etc.
These will differ from supplier to supplier and will depend on their business model and way of working – so it’s always important to understand the level of customer service a supplier will provide.
Taxed and levies
Taxes and levies are decided by Government and charged by suppliers to electricity and gas customers. They will be listed as a separate line and charge on your bill.
- Electricity: Public Service Obligation Levy (PSO Levy)
The PSO levy is a subsidy that all electricity suppliers are obliged by Government to apply to electricity customers in Ireland. It supports the generation of electricity from sustainable, renewable and indigenous sources.
The current PSO levy is €6.52 excl. VAT per month which equates to €78.24 excl. VAT or €88.80 per year inclusive of VAT.
- Gas: Carbon Tax
As a gas customer in Ireland, Carbon Tax will appear on your gas bill. Natural gas suppliers are obliged to add a carbon tax charge to all customers’ bills, which works out at 0.535 cents (including VAT) for every kWh of gas used.
- Value Added Tax (VAT)
VAT of 13.5% is paid on all domestic electricity and gas bills in Ireland and the overall cost will be detailed separately on your bill.
How to lower the cost of your energy bills
The quickest and easiest way to lower energy bills is to switch supplier. There can be a big difference in the cost energy suppliers pass through to their customers. In fact, it is possible to save €475 by switching electricity and gas supplier in Ireland.
At ‘Power to Switch’ we compare all tariffs, deals and offers across all suppliers to make sure you find the best deal. Switching is quick, hassle-free and means you keep more money in your pocket. You don’t even have to tell your old supplier you are leaving, making it even simpler.